Neoclassic Masterpieces
The neoclassical culture, especially the Greek, was one of the most influential cultural and artistic traditions in Western history. Emerging in the late 18th century as a reaction to Rococo and Baroque, neoclassicism represented a return to the ideals of simplicity, symmetry, and rationality of ancient Greece and Rome. The movement sought to recover the values of harmony, proportion, and objective beauty that characterized classical antiquity, having a profound impact on visual arts, architecture, philosophy, politics, and education. To this day, Greek neoclassical culture permeates art, design, and, increasingly, digital arts, reflecting a continuous reverence for principles of beauty, balance, and intellectual clarity.
Central Characteristics of Neoclassical Culture
- Valuation of Symmetry and Proportion: Inspired by Greek sculptures and buildings like the Parthenon, neoclassical artists sought to replicate the precise proportion and harmonious symmetry that defined Greek aesthetics. This translated into a return to clear and delineated forms, where every detail had its function and aesthetic purpose.
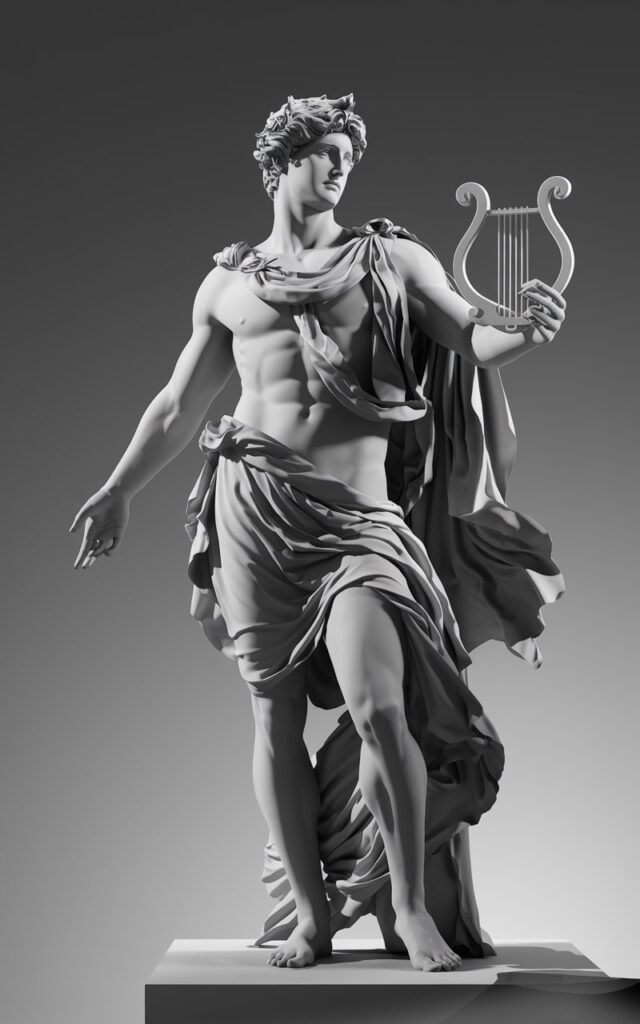
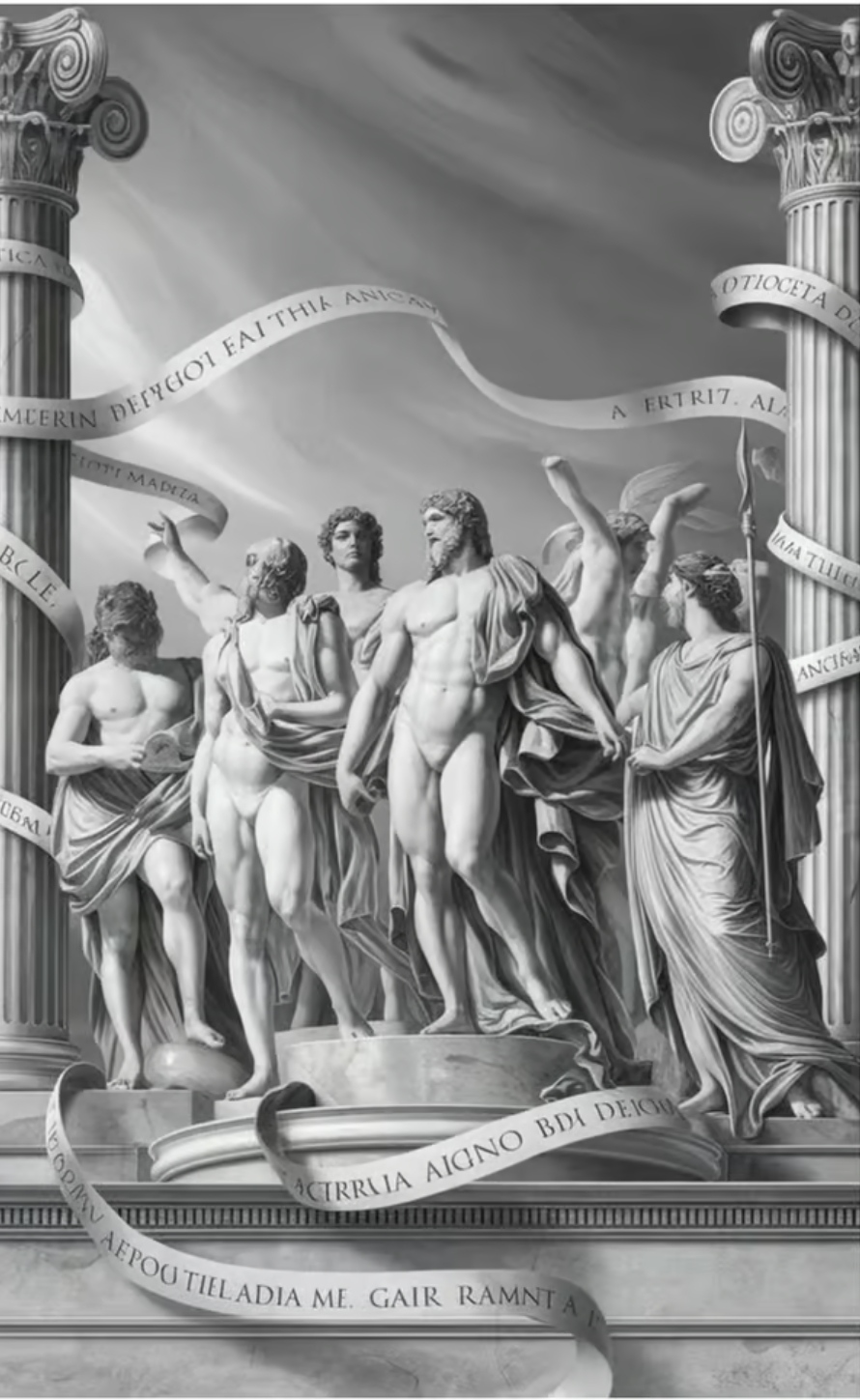
- Idealized Beauty: Neoclassical Greek art not only portrayed the human being but idealized it. Greek sculptures, such as those by Phidias and Praxiteles, were models of physical perfection, representing the human body at its peak of strength and grace. Neoclassicism adopted these same principles, depicting heroic characters and mythological figures with idealized beauty.
- Rationality and Intellectualism: Classical Greek culture also valued rationalism, the idea that reason and knowledge should guide life. This emphasis on logic and mental balance was reflected in the arts, where narrative and form obeyed rigorous rules of composition and clarity. Greek philosophy, especially the thoughts of Plato and Aristotle, also profoundly influenced the movement.
- Mythological Inspiration: Greek mythology was a rich source of themes and characters. In neoclassicism, artists and writers returned to figures like Apollo, Athena, and Hercules, using their stories as metaphors for virtue, courage, and morality.
The Influence of Greek Neoclassicism Today
Today, the ideals and aesthetics of Greek neoclassical culture continue to influence various spheres of society, from public architecture to digital arts. The presence of these elements can be observed in several forms of contemporary art, with special emphasis on digital design.
Architecture and Design
Public buildings in many world capitals are still heavily inspired by classical Greek architecture, with their Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian columns. Iconic structures like the United States Capitol and the Pantheon in Paris reflect the enduring influence of the symmetry and monumental sense of Greek culture. These principles also permeate contemporary digital design. Websites and apps often use layouts based on symmetry and proportion, reflecting the visual clarity and balance advocated by neoclassical culture.
In graphic and interface design, simplicity and clarity are principles derived directly from this heritage. The grids used to organize visual elements on websites and apps, for example, often follow a geometric logic that echoes the balanced visual organization of antiquity.
Visual Arts and Digital Media
Neoclassicism has also left a significant mark on contemporary visual arts. In the digital age, the idealized representations of the human body and Greek mythology continue to deeply influence the way characters are designed, especially in science fiction and fantasy settings. Video games, films, and animated series often draw on the aesthetics of classical antiquity to convey grandeur and heroism to their creations.
For example, video games like Assassin’s Creed Odyssey, which takes place in Ancient Greece, not only recreate architectural landscapes of the time but also adopt the sense of physical idealization and symmetrical perfection that characterized the classical portrayal of heroes and gods. The figures are modeled with detailed musculature and proportions reminiscent of Greek statues, reflecting the view of the human body as the personification of the ideal.
In digital illustration and concept art, the influence of neoclassicism manifests in the emphasis placed on precise anatomy and the use of chiaroscuro (light-dark contrast), which many digital artists use to give volume and depth to their creations, similar to the techniques developed by Greek sculptors to bring marble to life.
Cinema and Visual Effects
Neoclassical aesthetics also influence modern cinema, especially in epic and historical films. The digital recreation of structures and characters inspired by the classical past is an area where neoclassical principles are applied with great precision. Films like Gladiator and 300 not only revive heroic drama and mythical narratives but also visually recreate the proportion and idealized realism of Greek art. These productions often use CGI (computer-generated imagery) to create entire worlds based on neoclassical designs, from palaces and cities to statues and temples.
Moreover, the use of mythological figures in animation and visual effects carries the symbolic weight of Greek culture. Creatures like gods and monsters from mythology, now created through 3D modeling and advanced rendering, continue to resonate in contemporary themes and styles.
Digital Art and Virtual Sculpture
Sculpture, one of the most striking forms of expression in Greek culture, is also finding a new space in digital art. Virtual sculptures are created using 3D modeling programs like ZBrush and are widely inspired by the anatomical perfection of neoclassical sculpture. Today, digital artists can digitally sculpt characters and figures that evoke the grandeur and balance of Greek statues, applying realistic textures that simulate the marble or bronze used in antiquity.
Conclusion
Neoclassical culture, especially Greek, continues to exert a powerful influence on the arts and contemporary thought. Its ideals of harmony, proportion, and idealized beauty not only shaped the past but continue to shape the present, especially in the field of digital arts. The aesthetic rigor and intellectual clarity of ancient Greece find an echo in today’s advanced technologies, where the pursuit of visual and narrative perfection reflects a cultural continuity that began thousands of years ago, yet remains vibrant in the modern digital world.








Post Comment